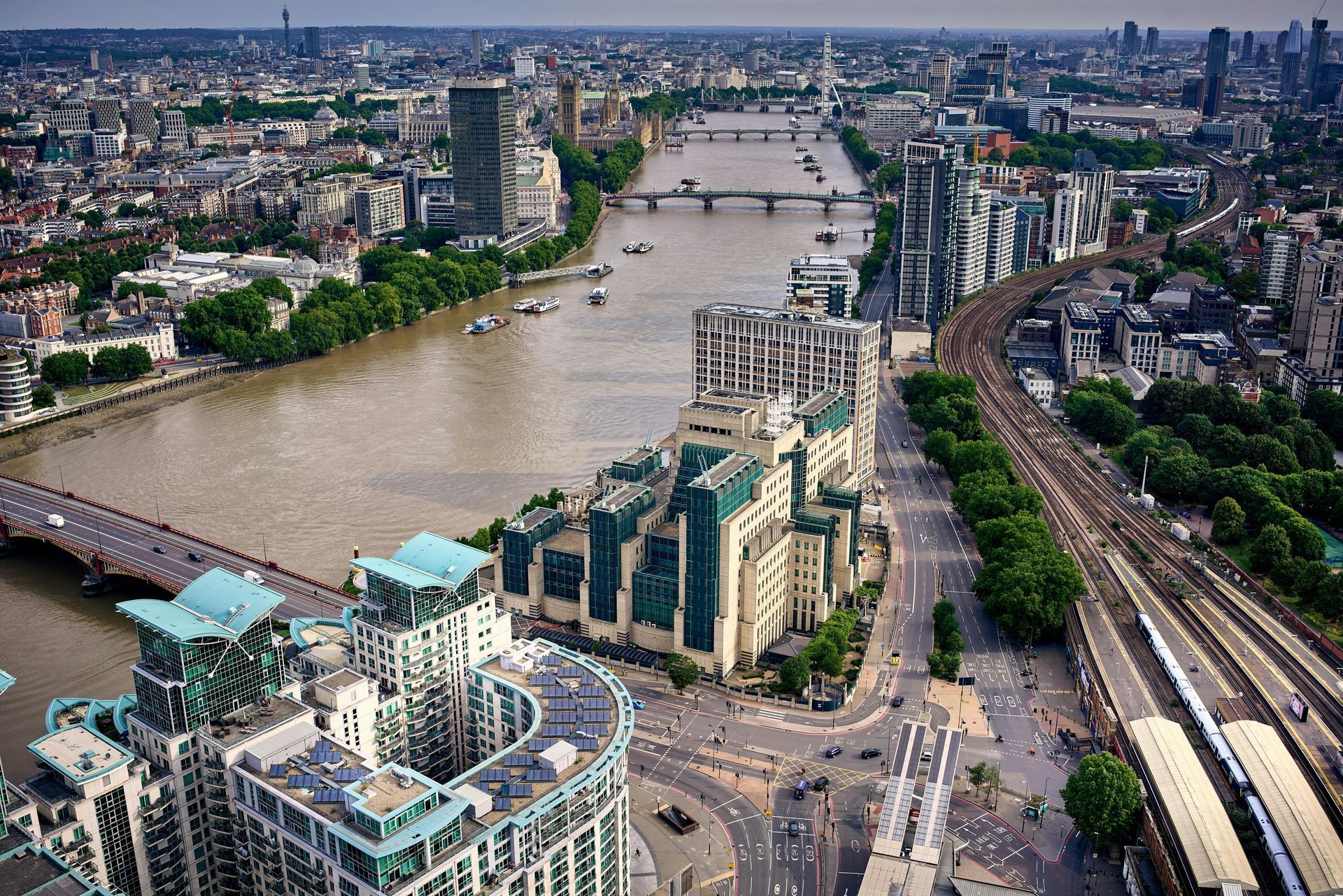
Budget 2024 - Labour’s Love Lost (for Non Doms) – Confirmed
Andy Wood • October 31, 2024
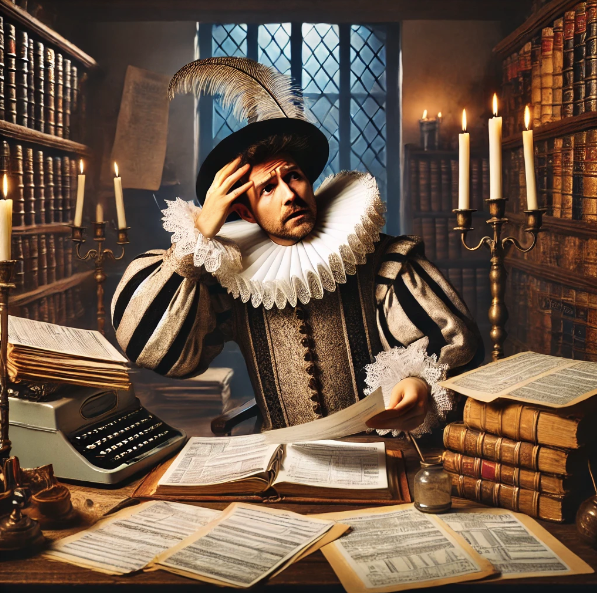

Labour’s Love Lost (for Non Doms) – Confirmed
Introduction
In it, the King and three of his best pals vow to avoid women. In true Shakespearean comedy, there is then a knock on the courtly door, and four women appear, and they fall in love.
Oh, the japes.
It seemed that after declaring their lack of affection for non-doms (following on from the Tories introduction of the destruction of the regime, lest we forget) might be softening in recent comment pieces. It was hardly becoming a love-in, but it seemed to be softening as the real financial impact of the changes.
But, as Shakespeare himself said on Radio 5 Live yesterday, “Alas, t’was not to be”.
You want to hear about the changes? Ok.
Abolition of the Remittance Basis
The main theme of the changes is the abolition of the UK’s long-standing remittance basis of taxation for non-doms.
An early form of this was first introduced by William Pitt the Younger in 1799.
If you think the remittance basis was an odd tax measure, it is worth knowing that Pitt also introduced taxes on servants, horses, non-working dogs, clocks and watches and hair powder.
However, in sum, the current remittance basis of taxation allows those who are non-UK domiciled (under general law) the privilege of leaving their foreign income and gains offshore without paying tax. As soon as they use or otherwise enjoy them in the UK, they then will pay tax on that amount.
Broadly speaking, domicile is a connection with a place which transcends physical presence (which, broadly, is residence). It is often described as the person’s ‘permanent’ home and is usually inherited from one’s father. It is difficult to ‘lose’.
Whether this is unfair or anachronistic is one point. But another is that it could be argued it has been highly successful in bringing internationally mobile wealth to the UK.
However, every dog has its day (or centuries) and it will be scrapped from 6 April 2025.
The New 4 Year FIG Regime
Thrust into this vacuum will be a new regime freshly drafted by the government. This will be a residence-based regime and will take effect from 6 April 2025.
Individuals who elect for this regime will not pay UK tax on foreign income and gains (FIG) for the first 4 years of tax residence.
It should be noted that this will only apply to those who are coming to the UK for the first time or have not been resident in the UK in any of the previous 10 tax years.
For those who became resident for tax purposes in 2022/23, 2023/24 and 2024/25 tax years (ie less than 4 years) they will be allowed to benefit for the regime until they have been resident for the balance of their first four years.
There is no separate charge on bringing those funds to the UK.
This means that those with significant, profitable overseas businesses (such that there wealth and income is outside of the UK) might find they have an opportunity to come to the UK for a period, be quite relaxed about whether they are UK resident and be quite relaxed about what they are bringing into the UK.
However, it should not be forgotten that this will be for a fixed four-year period only.
On the face of it, this looks particularly attractive, for example, footballers, sports persons and entertainers coming to the UK, with significant overseas income from endorsements and image rights. However, one should consider the scope of Draft 854H and “performance income”.
Inheritance Tax (IHT)
As we were told way back in the spring, the intention was not just to the abolition the remittance basis for income tax and CGT.
But also, to break the nexus between IHT and domicile.
This is perhaps a more surgical procedure, as IHT’s main connecting factor is domicile. So, what has the government come up with when it comes to the practical exercise of achieving this?
The appropriate nexus, replacing domicile, will be whether the person is “long term UK resident”.
The definition of a “long term UK resident” is if they have been resident in the UK for 10 out of the previous 20 tax years. For those under 20 years, the definition is slightly different.
As such, there are some advantages in not being such a person. I can hear the expats ears pricking as I write this. So, let’s have a look, eh?
If I have been living in, say, the UAE for over 10 tax years then I know I am not a long-term resident of the UK.
This means that I will only have a UK IHT exposure on my UK assets. Any foreign situs assets will be outside of the scope of UK IHT from 6 April 2025.
Many expats will already be under this understanding already (additionally, many believe they have NO UK IHT exposure at all!) but this would require them to have some confidence in their being non-UK domiciled under general law. The UAE has some difficulties in this regard as one cannot get permanent residence. However, as its unlikely they will have obtained any such confirmation from HMRC, the position is, at best, uncertain.
Under the new rules, there will be greater certainty as residence is an objective test.
For those that have come to the UK, once they have been resident for the 10 tax years, they will have a UK IHT exposure on their worldwide assets.
What about trusts, set up before the new regime, in this context?
Well, this is bad, bad news I am afraid.
At present, where a trust was settled by a non-domiciled (and non-deemed domiciled) individual, and the assets in the trust are foreign situs, then they are excluded property and outside the scope of UK IHT. This is the case even if the person settling the trust subsequently becomes deemed domiciled.
However, the government has confirmed the significant decision to provide no grandfathering where the settlor has become a long-term resident of the UK. This potentially brings significant amounts of wealth back into the UK IHT net.
This might well be a key consideration on whether a wealthy non-dom remains in the UK or decides whether any of their life in the UK can be conducted as a non-resident.
Of course, there will be a lag of up to 10 years before they escape the long-term UK resident designation.
It should be noted, that everyone, wherever they are domiciled, will be exposed to UK IHT on UK assets
– subject to reliefs and capital tax treaties.
These new rules will be effective from 6 April 2025.
Capital Gains Tax – rebasing
As well as the relief for new residents under the FIG regime, there are also changes for those who have previously benefited from the remittance basis regime.
Here, current and past remittance basis users will be able to rebase personally held foreign assets to 5 April 2017.
In other words, rather than the historic cost being brought into account for CGT purposes on sale, the market value of the asset in April 2017 will take its place.
This will generally be beneficial. But if it is not, then one can make an election for it not to apply to a particular disposal.
The Temporary Repatriation Facility (“TRF”)
A pertinent question is what happens to unremitted income and gains that is currently sitting in financial limbo – as, if remitted under the old regime, it would suffer UK taxes.
As a compromise, the so-called TRF was created.
Originally, when Labour announced its TRF, relevant non-doms would be able to remit foreign income and gains that arose before 6 April 2025 at a rate of 12%. This was only to be available in the tax years 2025-26 and 2026-27.
However, the government has announced that it will extending this to 3 years. It will expand the scope to offshore structures to sensible encourage non-doms to being their FIG into the UK.
The rate of tax for first 2 years the rate is 12% and will be 15% for final year. This seems to add unnecessary complexity but, it is assumed, this is to stop people dallying.
In some welcome news for non-doms, the TRF will also apply to distributions from trusts that were designated as protected trusts.
This would seem to be a bonus for those who are looking to extract the previous income and gains of those trusts at a ‘discount.’
Overseas Workday Relief (“OWR”)
At present, if a non-UK domiciled individual moves to the UK, becomes UK-resident, and works part of the year abroad, they can use OWR to exclude their foreign earnings from UK tax for those workdays spent overseas, provided the earnings remain offshore.
The Budget confirmed that OWR will be retained and reformed. It will be extended to a 4 year period (to match the new 4 year FIG regime) and remove the need to keep the income offshore.
The amount of relief that can be claimed each tax year will be limited to the lower of:
£300,000; or
30% of the employee’s net employment income.
Conclusion
So, with the flick of the Bard’s quill, the remittance basis is bade a fond farewell.
Well, not so much a flick of the quill, but heaps of more legislation.
There are some welcome provisions in there, such as the extension of the TRF. However, I feel the lack of grandfathering for trusts and the new IHT regime are a really egregious change. Will non-doms react, as predicted, by exeunt-ing stage left?
To quote Antonio in the opening lines of a Merchant of Venice, “in sooth, I know not why I am so sad”
Curtain.

Introduction More wealthy UK residents are exploring life overseas ahead of the 2026/27 tax year. Higher UK taxes, political uncertainty and a desire for a different way of living are all pushing people to look at alternatives. Four destinations stand out for high-net-worth UK individuals as at late 2025: 1. United Arab Emirates (Dubai) 2. Portugal 3. Switzerland 4. Malta Each offers a different blend of tax advantages, residency options and lifestyle. United Arab Emirates (Dubai) - Dubai is now the default choice for many UK entrepreneurs and professionals. Tax For individuals, there is currently no personal income tax on salaries, bonuses or most investment income, and no local capital gains or inheritance tax regime for individuals. There is VAT and a developing corporate tax regime, but personal tax remains far lighter than in the UK. The UK–UAE double tax treaty helps reduce the risk of the same income being taxed twice and needs to be considered alongside UK residence rules. Residency Common routes for UK nationals include: Employer- or company-sponsored residence visas Remote-worker visas for those employed or self-employed abroad Long-term “golden” style visas linked to investment, property or professional status Retirement options for over-55s. (All require private health insurance and periodic renewal.) Lifestyle Dubai offers a high standard of living, excellent connectivity and a large, well-established British community. Housing and schooling are expensive and the lifestyle can encourage overspending, but for many the tax position and opportunity outweigh the costs. Best for: Maximising net income and building or scaling a business in a dynamic, international city. Portugal - Portugal appeals to those who want EU residency, a milder climate and a slower pace of life. Tax The old NHR regime has closed to new applicants and been replaced by a newer incentive framework (often referred to as IFICI) aimed at certain professionals and activities. The UK–Portugal tax treaty reduces double taxation, and Portugal does not operate a classic wealth tax, though property-related charges can apply. (It's signed and ratified but not yet fully in force as of early 2026, which may slightly affect immediate tax planning). Residency Post-Brexit, common routes for UK nationals include: D7 visa – for those with sufficient passive income (pensions, investments, rentals). D8 / Digital Nomad visa – for remote workers with qualifying income from abroad. Work and other residence visas tied to employment or specific skills. These can lead to long-term residence and, ultimately, citizenship if physical presence and integration tests are met. Lifestyle Cost of living is generally below the UK (though higher in central Lisbon and the Algarve), English is widely spoken in cities, and the public and private healthcare systems are well regarded. There are large British and wider international communities. Best for: Those wanting EU residence, good quality of life and a balance of tax and lifestyle advantages. Switzerland - Switzerland attracts UK families who prioritise security, discretion and top-tier services. Tax Tax is set at federal, cantonal and communal level, so overall rates vary widely by canton. Well-chosen cantons can be very competitive for both individuals and companies. Private capital gains are not generally taxed, but there is an annual wealth tax on net assets, with rules depending on location. For suitable non-working individuals, some cantons still offer lump-sum (forfait) taxation, where tax is based on living costs rather than worldwide income, subject to minimum levels and conditions. Residency As non-EU nationals, UK citizens use: B permits – time-limited residence, often linked to work L permits – short-term residence for specific assignments C permits – longer-term settlement after sustained residence and integration Wealthy retirees and non-working individuals may be able to obtain residence based on financial self-sufficiency and, in some cantons, lump-sum taxation. Lifestyle High costs are offset by excellent infrastructure, schools and healthcare (with compulsory private health insurance). International communities are strong in Zurich, Geneva and other cities, though social life can feel more formal than Southern Europe. Best for: Those seeking stability, discretion and first-class public services and education, rather than the lowest day-to-day costs. Malta - Malta is a compact EU state with a very familiar feel for UK nationals: English is an official language and the legal and business environment is comfortable for British professionals. Tax Malta’s tax system and UK–Malta treaty can be particularly attractive where you hold significant foreign-source income. Under the Global Residence Programme, qualifying individuals can pay a favourable flat rate on foreign income remitted to Malta, while foreign capital gains kept offshore are generally not taxed in Malta. There is no separate wealth tax and no classic inheritance tax, though duties may apply to certain Maltese assets. The separate “golden passport” (citizenship by investment) route has been struck down by the EU’s top court, but residence programmes remain available. Residency Options for UK citizens include: Employer-sponsored Single Permits combining work and residence The Global Residence Programme for financially self-sufficient individuals meeting property and minimum tax thresholds Digital-nomad-style visas for remote workers Long-term residence after several years of compliant stay Lifestyle Costs (especially rent and property) are typically lower than in the UK outside the most fashionable areas. English is widely used in government and business, healthcare is solid, and London is only a short flight away. Best for: Those wanting an English-speaking EU base with favourable treatment of foreign-source income and a tight-knit expat community. How to decide & next steps - All four countries can work extremely well for UK high-net-worth individuals, but for different profiles: Choose Dubai if your priority is low personal tax on active income and you are comfortable with a high-energy city. Choose Portugal if EU residency, climate and lifestyle matter as much as tax. Choose Switzerland if stability, education and healthcare are at the top of your list. Choose Malta if you want an English-speaking EU base with flexible options for foreign income. The right answer depends on your overall wealth, income mix, family plans and how tied you remain to the UK. If you would like bespoke, confidential advice on whether remaining UK-resident or relocating to Dubai, Portugal, Switzerland or Malta is the better strategy for your situation, you are welcome to get in touch to explore your options in detail.